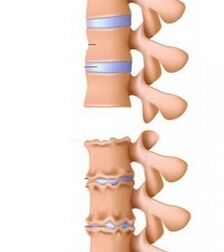
Osteochondrosis of the cervical region is a disease associated with a violation of metabolic processes, namely the accumulation of salts in the blood and lymph, which leads to the pathological transformation of the structure of the intervertebral discs, vertebrae and joints between the vertebrae.The loss of cartilage fabric of elasticity contributes to the displacement of the vertebrae, pinches of arteries and other dystrophic changes.
Due to the deformation of the joints, the height of the intervertebral discs decreases.It should be noted that in the cervical region the vertebrae are located closer to each other than in other parts of the spine, and therefore, the discs are in a healthy state.
Osteophytes (bone growths) form on the sides of the vertebrae, which irritate the muscles, causing their tension.Osteophytes also squeeze the spinal nerve roots, the vertebral artery and small blood vessels, from which the brain cells do not receive enough blood.The brain degrades and dies.
By the frequency of occurrence of osteochondrosis of the neck-in second place after the lumbar-cross.The first signs of the disease can appear at school age, after 25 years in one form or another this ailment is observed in almost everyone.In women aged 45–65, additional symptoms appear - tingling in the area of the hands during sleep against the background of pain and numbness.
The reasons for the development of osteochondrosis of the neck
Hypodynamia - a sedentary, sedentary lifestyle, mainly leads to cervical osteochondrosis.As a rule, they are suffered by people whose work involves a long stay in one position: work at the computer, office workers, drivers and so on.Osteochondrosis should be expected if a person has improper posture or he holds the body in an abnormal position for a long time, for example, holds a mobile phone or telephone with a shoulder.

Incorrect posture at the computer leads to cervical osteochondrosis!
Excessive stress of the back and neck cause excessive physical activity unusual for the body, for example, lifting weights.The same effect is obtained with incorrectly performing physical exercises.
Degeneration and dystrophy of the cervical region is due to constant nervous tension and stress, prolonged or temporary hypothermia of the body, unbalanced, meager nutrition, infections.
The group of increased risk belongs to people with a hereditary predisposition to osteochondrosis, with defects in the development of the spine, with a traumatic spine or back in general.The danger is chronic diseases of the musculoskeletal system (rheumatism, scoliosis, systemic lupus erythematosus).The disease is favored by hormonal imbalance, overweight, flat feet, progressive discos.
The main symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis and the factors causing them
The key symptom of osteochondrosis is pain in the occipital segment of the neck.If the nerve roots are affected, the pain extends to the shoulders, forearms.With spasm of muscles and impaired blood circulation, pain is felt in the ears, eyes, teeth, forehead.It can give in the shoulder blades, chest, gall bladder, lower back.Painful sensations increase even with minimal loads, long sitting, inclinations or turns of the head.The pain basically manifests itself after sleep and disappears if you develop muscles.Frequent departments occur - sharp pains, coupled with muscle hardening and difficulties in movement.

Numbness of arms and legs occurs, burns and tingling.Damaged roots with engine nerves weaken the strength of the muscles of the limbs.Blood pressure can rise, get the heart.
The cervical department with sophisticated intervertebral discs, osteophytes on the vertebrae and affected intervertebral joints creaks and crunches if you abruptly throw it or turn your head.
The strained arteries and the worsened blood supply to the occipital fraction of the brain and cerebellum leads to neurotic disorders, which manifests itself in the form of irritability, anxiety, variability of mood, resentment, and insomnia.There are outbreaks of anger, anorexia nervous, fear, longing.
For the same reason, the tongue and fingertips are numb, a voice wheezes, hearing and vision decreases, rustles in the ears, darkens in the eyes, fainting occurs.Almost always, especially in women, continuous headaches are observed, even stronger, if you sharply turn your neck.
The affected vestibular apparatus leads to disorientation in space, impaired coordination, dizziness and nausea and vomiting associated with these phenomena.
Stages of development of osteochondrosis of the neck
Cervical osteochondrosis develops stadially, each of the stages has its own clinical picture.
At the first stage (preclinical), the muscles are slightly tense, the pain is weak, when turning or tilting the head, it can increase.The rapid fatigue of the spinal and lumbar muscles is characteristic.At this stage, the disease is treated without medication.
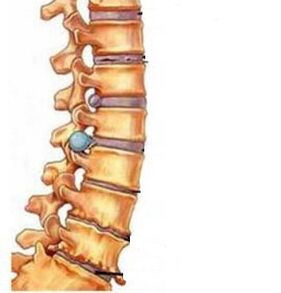
The second stage occurs with a decrease in the height of the intervertebral disc and pinching of the nerve endings.In addition to the neck, the shoulder and hand hurt.Fast fatigue, headache, distraction appears, work is difficult, and performance is reduced.
The third stage marks the formation of hernias of intervertebral discs.Then the muscles of the hands are weakening and numb, constant pain gives into the arm or shoulder.General weakness is accompanied by dizziness.
At the fourth stage, the vertebral artery is affected, the destroyed intervertebral disc is replaced by connective tissue.Coordination is disturbed, severe dizziness and the noise in the ears are worried.
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis by type and affected vertebrae
Several types of cervical osteochondrosis are distinguished.
- Rook syndrome- Due to the pinching of the nerve endings, the pain of high intensity, in addition to the neck, covers the shoulder, forearm, is felt in the shoulder blade and lower back.
- Vail artery syndrome- It is distinguished by a pulsating headache in the back of the head or temple.
- Irritative - reflex syndrome- burning pain in the neck and nape gives to the chest and shoulder, when turning the head, cough, in a dream it intensifies.
- Cardial syndromeIt occurs due to damage to the spine of the diaphragmatic nerve or large chest muscle.Pressing pains appear in the heart of the heart, they last for several hours, when moving or deep breathing, they intensify.
The defeat of different cervical vertebrae is manifested by its symptoms.
A striking 1st and 2nd cervical vertebra (CI-II) causes pain in the nape and crown.Pincreting the nerve root (C3) leads to numbness of the neck, the sensitivity of the tongue decreases, speech is disturbed.If the nerve spine of C4 is affected, the collarbone or shoulder is numb, breathing is disturbed, pain in the heart appears.Distrophy of the vertebra of the 5th department has a violation of the sensitivity of the arms and legs and pain in the shoulder.Compression of the roots of C6 and C7 is accompanied by pain in the neck, forearm, blade, lower back and back in general, weakening of the sensitivity of the hands and fingers.The affected nerve root of C8 provokes pain in the neck, back, elbow, and lower extremities.The little fingers are numb in their hands, the sensitivity of the skin decreases to zero.Due to the weakening of blood flow, the legs and hands become cyanotic.
Diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis
The diagnosis of the neck osteochondrosis begins with the collection of information about the lifestyle of a person and his work, the analysis of complaints and symptoms, it should also be found out whether this ailment was for relatives.
Then an external examination of the back and neck is carried out in different positions, which allows you to see if there are violations of posture.Palpation of painful zones reveals the degree of pain and tension of muscles and vertebrae.
The main role in the diagnosis is played by instrumental research methods.
The longest instrumental method - X -ray allows you to identify the general condition of the vertebrae and vertebrates, but in the later stages of the disease it is ineffective.
Computed tomography has much better diagnostic capabilities, but this method does not allow to make a complete idea of the presence and size of intervertebral hernias.It is not clear whether there is a compression of the hernia of the spinal cord.
The highest efficiency is shown by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).Not only bone formations are perfectly traced, but also other important structural elements of the spine: intervertebral discs, hernias, their parameters and how they develop.It is clear in what condition the soft fabrics are.Ultrasound duplex scanning of vertebral vessels allows you to make an idea of their structure, patency for blood flow and its speed, violations and abnormalities of the walls.
Having established damaged intervertebral discs and the degree of their violation, you can prescribe adequate treatment.Otherwise, not only osteochondrosis will progress, but different complications are possible.
Complications for cervical osteochondrosis
Complications for cervical osteochondrosis arise due to the effect on:
- discs, nerves, nerve endings, plexuses (neurological diseases);
- spinal cord;
- brain.
Closely placed nervous endings and blood vessels at the slightest disturbance are compressed, which, in turn, disrupts cerebral circulation, provokes a number of disorders and diseases: migraine, hypertension, heart impairment, problems with hearing, vision, and attention coordination arise.
The neglected cervical osteochondrosis is fraught with the development of the vertebral artery syndrome, brain ischemia, spinal stroke and other deadly pathologies.The growths on the vertebrae (radiculopathy) lead to complete or partial loss of sensitivity and mobility of the body.Squeezing the spinal cord causes a fatal outcome.
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the spine
With degenerative lesions of the intervertebral discs, I use different treatment methods depending on symptoms.
Drug treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
A specialist in osteochondrosis is a neuropathologist, a specialist directly on the spine is a vertebrologist.
Drug treatment is aimed at eliminating pain, relieving inflammation, improving blood circulation, supporting the body as a whole.
The most disturbing syndrome - severe, sometimes unbearable pain, can be removed using non -steroidal anti -inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).The same drugs relieve aseptic inflammation and swelling of the roots of damaged nerves.If the pain is weak, it is enough to take an analgesic.
You should know that most NSAIDs negatively affect the mucous membrane of the stomach, so it is not recommended to take them for a long time.
Anesthetize and simultaneously warm the affected areas can be ointments and gels.A pepper patch can be applied to the sore spot, but its effect is limited to warming up the inflamed area.
Diuretics and infusions of herbs are suitable for combating edema.
In the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis, B vitamins are certainly used (B1, B6, B12).Vitamins of this group improve metabolic processes in nervous tissue.Effective both oral tablets and solutions for intramuscular administration are effective, but injection administration is painful and can have complications.
The most important therapeutic task is the restoration of cartilage in the intervertebral disk.It is solved using chondroprotectors.It must be borne in mind that all these drugs are biologically active additives with vague effectiveness.
Features of pathology require the use of drugs that improve blood properties, blood flow to the brain, and the nutrition of damaged nerve roots.
Muscle cramps can be removed by resorting to muscle relaxants.
Medicines introduced into the body through intramuscular injection affect the nerve endings faster.Blocks are carried out directly in the affected area, which promptly provides the required effect.
The duration of taking certain drugs depends on the stage of osteochondrosis, complaints of the patient and his related diseases.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis without fail includes physiotherapeutic procedures.
Under the influence of electric current (electrophoresis), the medicine immediately enters the destruction site.
The effect of ultrasound anesthetizes, relieves inflammation, improves metabolic processes.Magnetotherapy relieves tissue edema and, thus, reduces pain.Laser therapy has an anti -inflammatory effect and improves blood circulation.
To improve the blood supply to the brain, massage of the cervical zone is very useful.A special place in the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis is occupied by therapeutic exercises, especially if numbness of the limbs is observed.The patient's condition improves by improving blood circulation and reducing muscle stress.In the acute phase of the disease, gymnastics is not recommended, it should be done during the recovery.
If conservative treatment does not give a positive result within 6 months, pain does not pass and damaged nerve roots do not restore, or myelopathy manifested, you can resort to surgical intervention.
With the not -eliminated root cause of osteochondrosis of the cervical region, and this is in most cases a sedentary, sedentary lifestyle, drug treatment will have a short -term effect.For irrevocable recovery, regular physical activity and nutrition that does not contribute to the development of the disease are needed.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis with folk methods
For the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis, products of plant and animal origin are used.They can be taken inside and applied outside.

For internal use, you can prepare an infusion of celery, a bay of 4-5 g of plants with a liter of boiling water and insisting for 2-4 hours.
The compress can be prepared from:
- honey (1-2 teaspoons) and mummy;Heat, put on a warm woolen fabric and attach to the affected area of the spine at night;
- crap;Grate the root on a grater, heat a little, wrap in gauze to be applied to a sore spot and tie it with a warm cloth to maintain heat;
- burdock(Rinse the leaves with hot water, apply in a sore spot and wrap with bandage when the leaves dry, replace with new ones).
For rubbing, you can use chamomile and oil (preferably olive), although sunflower is also suitable.30 g of flowers and 0.5 liters of oil over low heat to boil, insist 2 days, strain and apply to sore areas.To the chamomile you can add St. John's wort, calendula, celandine.
For the same purposes, you can prepare a decoction of dandelion, birch buds, mint, coriander leaves (combine the mixture with steep boiling water in a ratio of 1: 1, insist an hour, after rubbing, apply a warming bandage).A means of rubbing from calendula (50 g of flowers pour 0.5 liters of vodka, insist 2 weeks).
To get rid of symptoms of osteochondrosis, leeches - hirudotherapy have long been used.In the early stages, 6 sessions are enough.But leeches can cause allergies and then, of course, treatment ceases.
Folk remedies show effectiveness only at the initial stage of the disease, if the disease progresses, the basis of treatment should be drug methods.
Prevention of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
The main preventive measure from this disease is physical activity (including walks, swimming) and gymnastics (aerobics, yoga), but you cannot raise excessive severity.Bodybuilding can provoke the protrusion of the cervical disk.Support at the proper level of weight is fraught with this measure.When sitting, you need to monitor the posture, after every hour take five -minute breaks, knead the neck every 2 hours.But sharp movements of the head should be avoided.If you regularly do massage, it will be possible to prevent the development of excessive muscle tension.

Food should be rich in vitamins, minerals (calcium, magnesium) and other beneficial substances.Porridge, eggs, legumes, mushrooms, low -fat meat are recommended (beef, chicken, rabbit), seafood (fish, crabs, oysters, lobsters, mussels), dairy products (milk, cottage cheese), fresh fruits, fresh vegetables (cabbage, carrots, eggplant, tomatoes, cucumbers, pepper, beets, bow, bow, bow, bow, bow, bow, bow, bow, bow, bow, bow, bow, bow, bow, bow.broccoli, celery, spinach), nuts, hazelnuts, almonds.
If the neck osteochondrosis is accompanied by atherosclerosis, it is necessary to limit the use of products that contain cholesterol - animal fats, fatty meat, fatty milk products.Limited consumption products also include flour products, sugar, salt.
Alcohol is harmful in that, falling into the blood, it destroys the cells, which worsens the already poor blood circulation.Smoking also falls under the ban.
To protect osteochondrosis, stress must be avoided.A healthy sleep is made to prevent the development of the disease.You need to sleep on a solid mattress and low pillow, the neck should not bend more than 15 °.
Hot shower, a sauna and a bathhouse help to remove the neck spasms.
If there is a predisposition to osteochondrosis, the doctor should be shown from time to time.



















